Research Highlights
Copper-Photoredox-Catalyzed Divergent Strategy for the Site-selective Arylation and Alkylation of Glycines and peptides. P. Meher, M. S. Prasad, K. R. Thombare, and S. Murarka* ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 18896-18906.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscatal.4c06254
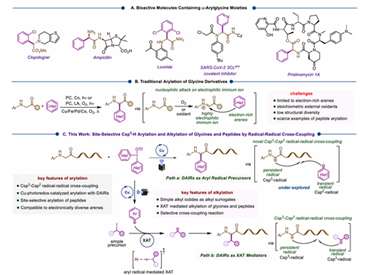
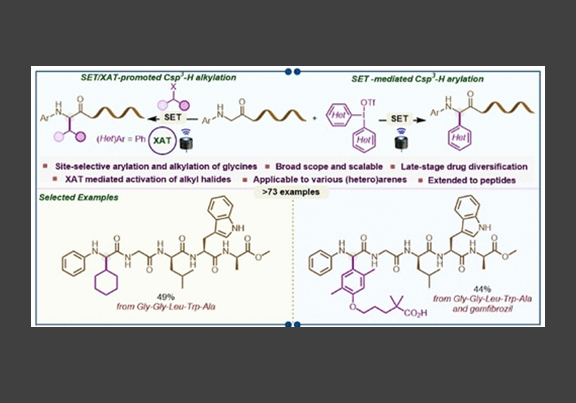
There is a scarcity of general strategies for the site-selective α–Csp3–H arylation of glycine derivatives to synthesize nonproteinogenic α-arylglycines that occur frequently in commercial drugs and bioactive molecules. We disclose a copper-photoredox-catalyzed site-selective α–Csp3–H arylation of glycine derivatives using diaryliodonium reagents (DAIRs) as arylating agents. This strategy harnesses the underexplored ability of DAIRs to serve as arylating agents under visible-light irradiation using copper salts as photocatalysts. The method applies to the glycine-selective C–H arylation of peptides with electronically and structurally diverse DAIRs. Moreover, we demonstrate that the photoinduced copper-catalyzed single electron transfer (SET) strategy can be coupled with the halogen atom transfer (XAT) process in the presence of alkyl iodides to accomplish site-selective α–Csp3–H alkylation of glycines and peptides. In this synergistic SET/XAT approach, phenyl radicals generated from diphenyl iodonium triflate mediate the XAT process to generate alkyl radicals from alkyl iodides. Both of these methods operate under mild conditions and exhibit broad scope with appreciable functional group tolerance. Overall, the divergent toolbox strategies presented here facilitate access to various alkylated and arylated glycines and peptides and enable bioconjugation between peptides and drug molecules.